|
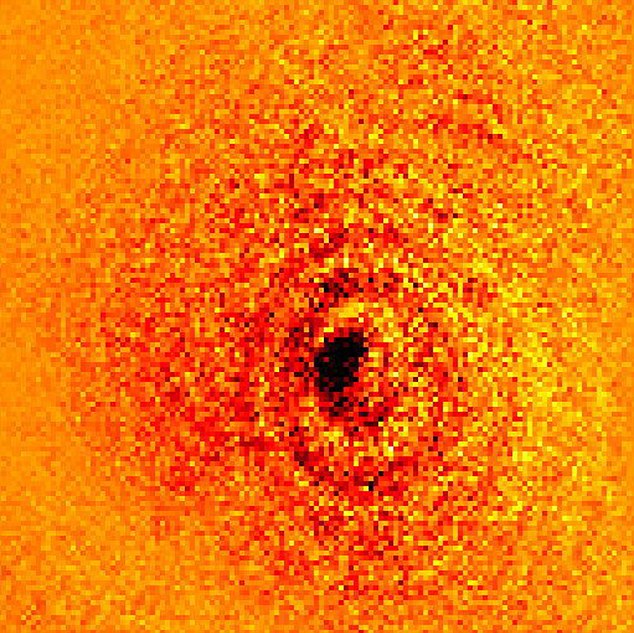
So, just how many atoms does it take to cast a shadow then? Only one, it seems...  Dave Kielpinski: scientist Dave Kielpinski: scientist The amazing photograph of the shadow of a single Ytterbium atom has opened up a whole spectrum of possibilities for the scientific world. The image is “the first absorption imaging of a single atom isolated in a vacuum.” Professor Dave Kielpinski, from Griffith University’s Centre for Quantum Dynamics in Brisbane, said that “we have reached the extreme limit of microscopy; you cannot see anything smaller than an atom using visible light.” It was not an easy task, though: “if we changed the light we shined on it by just one part in a billion, the image could no longer be seen.” Griffith University is the only place in the world with a super high-resolution microscope capable of creating a shadow dark enough to be captured. The team at Griffith chose Ytterbium as the subject of the experiment it had “the right internal structure to allow us to do quantum computing,” according to team member Ben Norton, thus enabling them to build a laser of the exact colour to excite the atom. The atom itself was isolated in a chamber, and held in place by electrical forces: a process in itself not new to science, but difficult to accomplish. The results of all this precision and patience could revolutionize some of the imaging practices in exsitence today. Kielpinski noted in the published paper that the “absorption of photons by single atoms is of immediate interest for quantum information processing,” while it “also point out new opportunities in imaging of light-sensitive samples both in the optical and X-ray regimes.” As fellow team member Dr Erik Streed says, “this is important if you want to look at very small and fragile biological samples such as DNA strands where exposure to too much UV light or x-rays will harm the material” as “we can now predict how much light is needed to observe processes within cells, under optimum microscopy conditions, without crossing the threshold and destroying them."
0 Comments
MRI imaging techniques increase understanding of the Sun's interior plasma motions and convection currents. 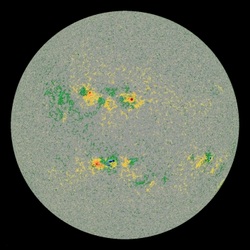 © NASA © NASA Scientists from NYU's Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and its Department of Physics, Princeton University, the Max Planck Institute, and NASA, have come together to produce MRI images of the Sun's internal plasma motions which significantly increase our understanding of how convection currents progress from deep within its structure to the surface. As the Sun is opaque, this convection is not normally observable. It also poses significant questions regarding our understanding of sunspot formation and magnetic field generation. The research, undertaken from images taken from a 16-million pixel camera, produced readings which seemed to show that "convective velocities are 20 - 100 times weaker than current theoretical estimates." (1) This was done by deducing the motion of the hidden plasma currents beneath the surface of the Sun from the images of movements from its surface. Shravan Hanasoge, an associate research scholar in geosciences at Princeton University and a visiting scholar at NYU's Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences, said the results that if they "are indeed that slow in the Sun, then the most widely accepted theory concerning the generation of solar magnetic field is broken, leaving us with no compelling theory to explain its generation of magnetic fields and the need to overhaul our understanding of the physics of the Sun's interior." For more information, click here, and see the video below. (1) Anomalously Weak Solar Convection, Shravan M. Hanasoge and Thomas L. Duvall, Jr. and Katepalli R. Sreenivasan, 14/06/2012.
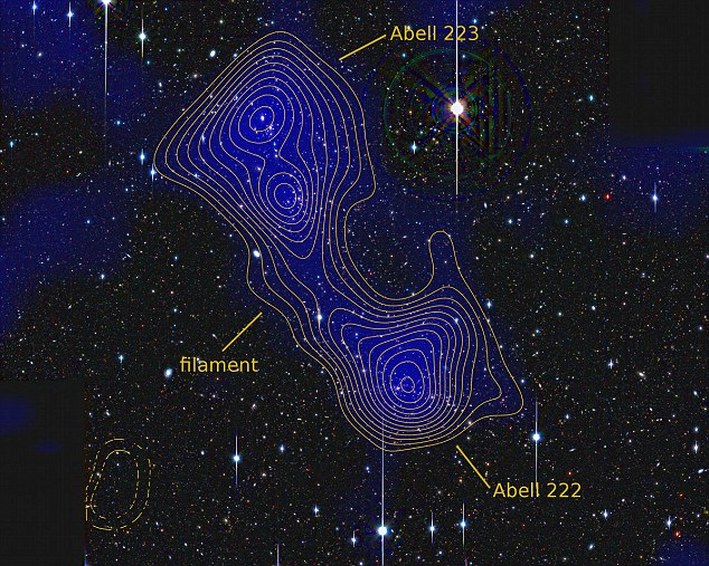
Dark matter structure observed for the first time as scientists discover a dark matter filament between two clusters of galaxies about 2.7 billion light-years away.  Jörg Dietrich: physicist Jörg Dietrich: physicist For something that makes up an estimated 84% of the universe (1), dark matter is a pretty elusive substance: until now, that is. Scientists have observed a filament of dark matter connecting galaxy clusters Abell 222 and Abell 223, almost 2.7 billion light-years away. The presence of dark matter has been detected by monitoring the way large clumps of it, located in galaxy clusters, bend light. This phenomenon is more difficult to observe with the filaments which are thought to connect the various clusters, much like a spider's web, as they have a much smaller mass. The observation published in Nature Magazine this week - which was made by Jörg Dietrich, a cosmologist at the University Observatory Munich in Germany, and his colleagues - was of a massive filament which was "oriented so that most of its mass lies along the line of sight to Earth." (2) In the published Abstract we are told that "[i]t is a firm prediction of the concordance cold-dark-matter cosmological model that galaxy clusters occur at the intersection of large-scale structure filaments." (3) Dietrich goes on to say that the discovery "'is the first time a dark matter filament has been convincingly detected" and that it is "a resounding confirmation of the standard theory of structure formation of the universe...and a confirmation people didn't think was possible at this point." (4) A new particle has been discovered at CERN which is consistent with the theoretical attributes of the long coveted Higgs-Boson or "God" particle.  Peter Higgs: scientist Peter Higgs: scientist After 45 years of searching, scientists at CERN have publically stated that a particle with properties consistent with the theoretical characteristics of the Higgs-Boson has been discovered in the LHC. The combination of two separate data sets from the ATLAS and CSM experiments has left the discovery with a five-sigma point confidence level - meaning that there is a one-in-3.5 million chance that the result could have occurred for reasons other than the Higgs-Boson particle. Both experiments observe a new particle in the mass region around 125-126 GeV, which scientists believe to be, beyond doubt, a new particle: "We know it must be a boson and it’s the heaviest boson ever found" said CMS experiment spokesperson Joe Incandela. The video below is a compilation of snippets of interviews with Peter Higgs, Francois Englert, Carl Hagen and Gerald Guralnik after the discovery. For further information, please see the official CERN press release, the BBC website, the Guardian website, and the videos below: |
Categories
All
Archives
November 2013
|
MOST VIEWED POSTS
© James Edward Hughes 2013
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed





